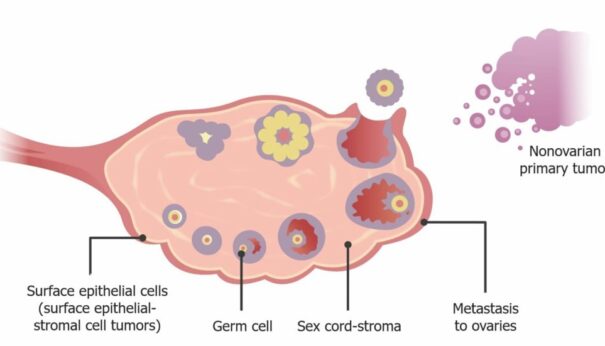
 Epithelial tumors are called carcinomas. They are about 90% of all ovarian cancer diagnoses, and 70% of patients with this type of cancer are diagnosed in advanced stages.
Epithelial tumors are called carcinomas. They are about 90% of all ovarian cancer diagnoses, and 70% of patients with this type of cancer are diagnosed in advanced stages.
There are 4 main categorizations of epithelial carcinomas. Each subtype shares specific traits that can be identified when looking at the tumor cells under a microscope.
- Serous Carcinoma
- High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma (HGSOC): About 75% of all epithelial cancers are HGSOC.
- Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma (LGSOC): Low-grade tumors are generally slower growing and less aggressive than high-grade tumors, however they are less common.
- Mucinous Carcinoma: About 6% of all epithelial cancers are mucinous carcinomas.
- Endometrioid Carcinoma: Endometrioid carcinoma can be high or low grade, but for this subtype, low grade is more common. Endometrioid carcinomas are about 10% of all epithelial cancers.
- Clear Cell Carcinoma: About 6% of all epithelial cancers are clear cell carcinomas.
 Germ cell tumors start in the ova, eggs, or the female ovary. They account for less than 2% of all ovarian cancers.
Germ cell tumors start in the ova, eggs, or the female ovary. They account for less than 2% of all ovarian cancers.
There is usually a more positive prognoses for patients diagnosed with this type of ovarian cancer. 9 out of 10 patients survive 5 years or more after their diagnosis.
Germ call tumors can be a single subtype or a mix of subtypes:
- Teratomas – Malignant, immatures teratomas are often found in girls younger than 18.
- Dysgerminomas – The most common form of germ cell ovarian cancer, and commonly found in women in their teens and twenties. Most dysgerminomas are slower growing.
- Endodermal Sinus Tumors – They spread rapidly but are usually very sensitive to chemotherapy.
- Choriocarcinomas – Like sinus tumors, they are usually fast growing but sensitive to chemotherapy.
 Stromal cell tumors start in the tissue cells that produce the female hormones of estrogen and progesterone. This type of ovarian cancer is the least common type of all ovarian cancers.
Stromal cell tumors start in the tissue cells that produce the female hormones of estrogen and progesterone. This type of ovarian cancer is the least common type of all ovarian cancers.
Vaginal bleeding is one of the most common symptoms for stromal cell tumors.
More than half of stromal cell tumors are found in women over 50 years of age, but about 5% of cases do occur in young girls.
Stromal cell cancer is usually caught at an early stage, and patients have a positive outlook with more than 75% of patients surviving long-term.
The malignant subtypes include:
- Granulosa cell tumors – The most common subtype of stromal cell ovarian tumors.
- Granulosa-theca tumors
- Sertoli-leydig tumors
Type of Ovarian Cancer |
Proportion of Ovarian Cancer Tumors |
Commonly Affected Age Group |
Primary Subtypes of Tumors |
| Epithelial | 90% | Post-menopausal women | Serous, Mucinous, Endometrioid, Clear Cell |
| Germ Cell | <2% | 10-30 years | Teratoma, Dysgerminoma, Endodermal Sinus Tumors, Choriocarcinoma |
| Stromal Cell | 1% | Perimenopausal women | Granulosa cell tumors, Granulosa-theca tumors, Sertoli-Leydig tumors |
MORE INFORMATION ABOUT OVARIAN CANCER CAN BE OBTAINED AT:
National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health
cancer.gov/types/ovarian
U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
cdc.gov/cancer/ovarian
American Cancer Society
.cancer.org/cancer/types/ovarian-cancer

